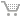
Universal Astrolabe de Rojas


Our price: $ 398.00
 Free Shipping to Continental U.S.
Free Shipping to Continental U.S.
In Stock
Our price: $ 398.00
(Free U.S. Shipping)
In Stock
- Details
- Delivery
- More Infos
- Reviews
Diameter: 8 inch (20 cm)
Overall height: 10 inch (25 cm)
Weight: 1.62 kg (3.6 lb)
Materials: lacquered metal
Universal Astrolabe de Rojas.
Reproduction of an universal astrolabe realized in accordance to Juan de Rojas y Sarmiento in the 16th century.
The Spanish astronomer and mathematician Juan de Rojas y Sarmiento presented to the European public the Orthographic Projection (1550).
This projection was successfully applied in this universal astrolabe that offered remarkable advantages over its predecessors because it could be used in any latitude.
Function.
An astrolabe is a very ancient astronomical computer for solving problems relating to time (what time is it ?) and the position of the Sun and stars in the sky.
Astrolabes are used to show how the sky looks at a specific place at a given time.
This is done by drawing the sky on the face of the astrolabe
To use an astrolabe, you adjust the moveable components to a specific date and time. Once set, much of the sky, both visible and invisible, is represented on the face of the instrument.
Typical uses of the astrolabe include finding the time during the day or night, finding the time of a celestial event such as sunrise or sunset and as a handy reference of celestial positions.
The typical astrolabe was not a navigational instrument although an instrument called the mariner's astrolabe was widely used in the Renaissance.
History.
The history of the astrolabe begins more than two thousand years ago.
The principles of the astrolabe projection (stereographic projection) were known before 150 B.C., and true astrolabes were made before A.D. 400.
The astrolabe was highly developed in the Islamic world by 800 and was introduced to Europe from Islamic Spain (al-Andalus) in the early 12th century.
It was the most popular astronomical instrument until about 1650, when it was replaced by more specialized and accurate instruments.
Accuracy.
The sky map of this astrolabe is the one of the 21th century.
This universal astrolabe is fully functional.
It's accuracy is:
 for the Northern latitudes,
for the Northern latitudes,
 for the Southern latitudes.
for the Southern latitudes.
Attention to detail, historical interest, beauty of forms characterize this very fine Astrolabe, shipped complete with a hardwood display stand and a user guide with ad hoc exercises (


 ).
).
Overall height: 10 inch (25 cm)
Weight: 1.62 kg (3.6 lb)
Materials: lacquered metal
Universal Astrolabe de Rojas.
Reproduction of an universal astrolabe realized in accordance to Juan de Rojas y Sarmiento in the 16th century.
The Spanish astronomer and mathematician Juan de Rojas y Sarmiento presented to the European public the Orthographic Projection (1550).
This projection was successfully applied in this universal astrolabe that offered remarkable advantages over its predecessors because it could be used in any latitude.
Function.
An astrolabe is a very ancient astronomical computer for solving problems relating to time (what time is it ?) and the position of the Sun and stars in the sky.
Astrolabes are used to show how the sky looks at a specific place at a given time.
This is done by drawing the sky on the face of the astrolabe
To use an astrolabe, you adjust the moveable components to a specific date and time. Once set, much of the sky, both visible and invisible, is represented on the face of the instrument.
Typical uses of the astrolabe include finding the time during the day or night, finding the time of a celestial event such as sunrise or sunset and as a handy reference of celestial positions.
The typical astrolabe was not a navigational instrument although an instrument called the mariner's astrolabe was widely used in the Renaissance.
History.
The history of the astrolabe begins more than two thousand years ago.
The principles of the astrolabe projection (stereographic projection) were known before 150 B.C., and true astrolabes were made before A.D. 400.
The astrolabe was highly developed in the Islamic world by 800 and was introduced to Europe from Islamic Spain (al-Andalus) in the early 12th century.
It was the most popular astronomical instrument until about 1650, when it was replaced by more specialized and accurate instruments.
Accuracy.
The sky map of this astrolabe is the one of the 21th century.
This universal astrolabe is fully functional.
It's accuracy is:
 for the Northern latitudes,
for the Northern latitudes,
 for the Southern latitudes.
for the Southern latitudes.
Attention to detail, historical interest, beauty of forms characterize this very fine Astrolabe, shipped complete with a hardwood display stand and a user guide with ad hoc exercises (
Delivery date of the Universal Astrolabe de Rojas *

* indicative date for an order validated today.
Guarantees for the Universal Astrolabe de Rojas
 Satisfaction Guarantee
Satisfaction Guarantee
 Direct Guarantee: 1 year
Direct Guarantee: 1 year


Complete TED video (9 minutes)
Introduction, description: different components, stereographic projection, main function: how to get time in 5 steps, other functions, history, conclusion.
 View video
View video
Video showing the different parts of an astrolabe (2 minutes)
Mater, Alidade, Plate, Altitude, Azimuth, Horizon, Zenith, Tropic and Equator, Rete, Ecliptic, Fixed Stars.
 View video
View video
Customer reviews of the H34
(ordered by decreasing date) Average of 4,4 based on 17 reviews.
Average of 4,4 based on 17 reviews.
 Article comment
Article comment
 Gregor S. from 9250 Gornja radgona (Slovenia)
Gregor S. from 9250 Gornja radgona (Slovenia)
 Nice item and made in precision sufficient for learning and making observations.
Nice item and made in precision sufficient for learning and making observations.
 Jyrki J. from 00530 Helsinki (Finland)
Jyrki J. from 00530 Helsinki (Finland)
 4,4 on 5 (17 reviews)
4,4 on 5 (17 reviews)2 last reviews
 Article comment
by Gregor S. from 9250 Gornja radgona
Article comment
by Gregor S. from 9250 Gornja radgona
 Nice item and made in precision sufficient for learning and making observations.
by Jyrki J. from 00530 Helsinki
Nice item and made in precision sufficient for learning and making observations.
by Jyrki J. from 00530 Helsinki